MVP Development Services for Startups & Guide: How to Build a Minimum Viable Product in 2025
Launching a product without validation is a costly gamble. This 2025 guide walks startups through building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP) that’s lean, scalable, and ready for global markets. Whether you're based in Kenya, Europe, or Silicon Valley, learn how to validate ideas, gather feedback, and launch faster with a step-by-step MVP strategy backed by real case studies and agile principles.
Posted on May 30, 2025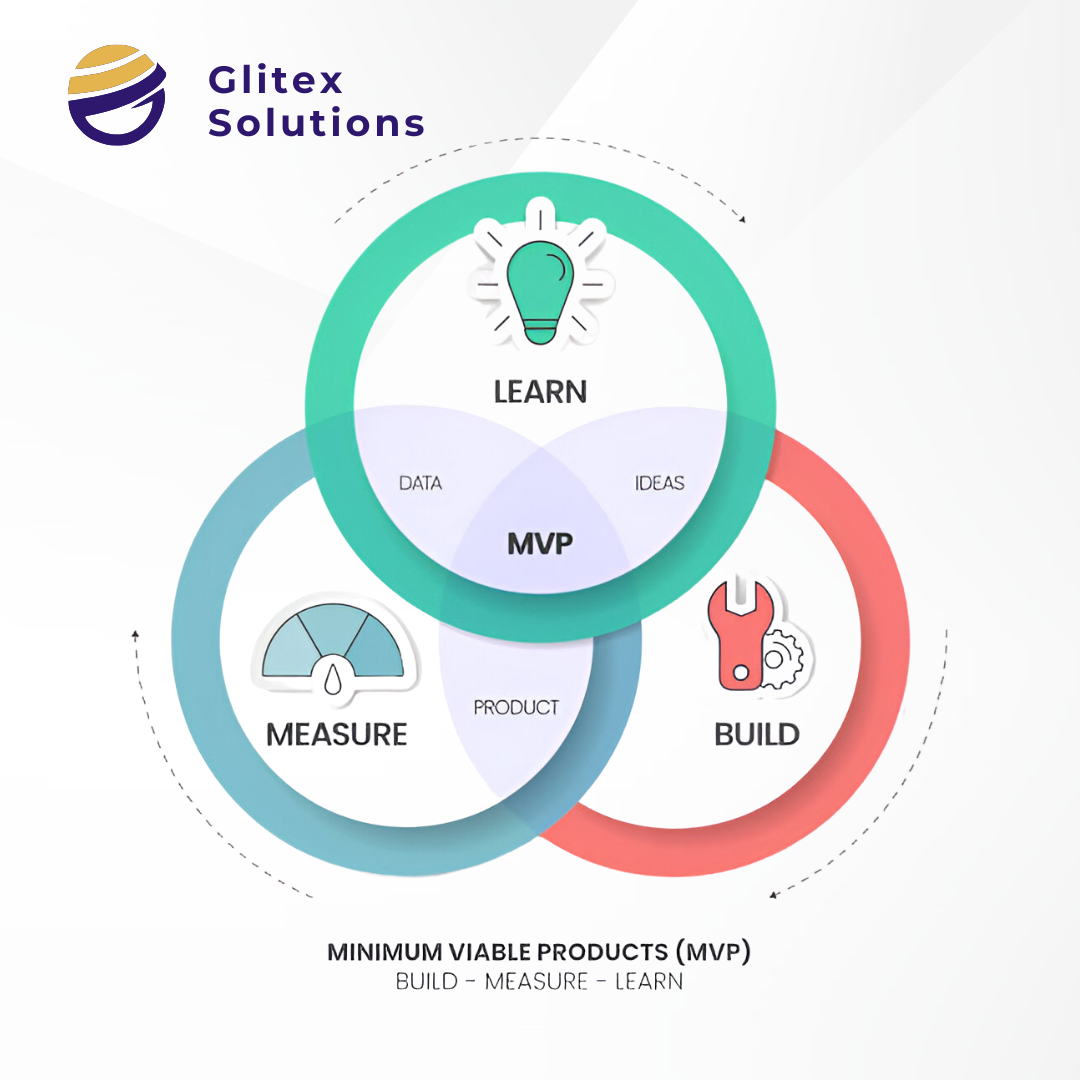
In the dynamic startup ecosystem of 2025, launching a product without validation can lead to significant resource wastage. Developing a Minimum Viable Product offers a strategic approach to test core functionalities, gather user feedback, and refine the product accordingly.
What is an MVP?
A Minimum Viable Product (MVP) is the most basic version of your product that still delivers value to early adopters. It focuses on essential features necessary to solve a specific problem, allowing for assumption testing and feedback gathering all with minimal resource investment.
🔍According to CB Insights, 42% of startups fail due to a lack of market need. A gap MVPs are designed to address.
Why MVP Development is Crucial for Startups
1. Accelerated Market Validation
Test core functionalities with real users, gather insights, and validate demand before a full-scale launch.
Startups that validate their product idea through an MVP are 3x more likely to pivot successfully and find product-market fit. (Harvard Business Review)
2. Cost Efficiency
Reduce development costs by focusing only on must-have features, avoiding overspending on invalidated ideas.
Building an MVP can cut development costs by up to 60%, compared to full-scale builds. (Lean Startup methodology)
3. Enhanced Investor Appeal
Demonstrate traction and real-world interest with a working product, even if it’s not perfect.
67% of successful startups began with an MVP before attracting investors. (Startup Genome Report)
4. Facilitates Agile Development
Supports iterative development cycles — allowing startups to adapt quickly to user needs and market changes.
Companies that apply agile methods during MVP development see 2x faster feature rollouts. (Agile Alliance)
5. Integration with Emerging Technologies
Early MVPs allow for experimental integration with AI, machine learning, or personalization features to create scalable, user-centric solutions.
Over 80% of startups incorporating AI in their MVPs reported improved user experience and retention. (PwC AI Report)
Step-by-Step Guide to Building an MVP
1. Identify the Core Problem
Clearly define the pain point your product is solving. Ensure it's narrow enough to validate quickly, but impactful enough to matter.
2. Conduct Market Research
Analyze competitors, review user behavior, and evaluate trends to validate your assumptions.
3. Define the Target Audience
Develop user personas that reflect your ideal customers — their needs, behaviors, and motivations.
4. Outline the User Journey
Map out the typical flow users would take while interacting with your product, from onboarding to core functionality.
5. List Essential Features
Cut non-essentials. Focus on what your MVP must do to solve the primary problem.
6. Develop the MVP
Use agile methodologies and low-code or no-code tools where applicable to launch fast and learn quickly.
7. Test and Gather Feedback
Roll out to early adopters or beta testers. Use surveys, heatmaps, and usage analytics to assess performance.
8. Iterate and Enhance
Use real-world data to refine features and resolve friction points. Improve in short cycles.
9. Plan for Scaling
Once validated, build a product roadmap for feature expansion, team scaling, and market outreach.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overcomplicating the MVP: Adding too many features upfront confuses users and dilutes your value.
- Neglecting User Feedback: Ignoring real user input can lead to building features no one wants.
- Skipping Market Research: Making assumptions without data leads to poor product-market fit.
- Under-communicating Value: If users don’t understand the MVP’s value immediately, adoption will suffer.
Need Help Building an MVP?
Let’s talk strategy, tools, or team structure.
